3 minutes
Service mesh & lstio
What’s service mesh
A service mesh, like the open source project Istio, is a way to control how different parts of an application share data with one another. Unlike other systems for managing this communication, a service mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer built right into an app
How it works
A service mesh doesn’t introduce new functionality to an app’s runtime environment — apps in any architecture have always needed rules to specify how requests get from point A to point B. What’s different about a service mesh is that it takes the logic governing service-to-service communication out of individual services and abstracts it to a layer of infrastructure.
To do this, a service mesh is built into an app as an array of network proxies. Proxies are a familiar concept in enterprise IT.
In a service mesh, requests are routed between microservices through proxies in their own infrastructure layer. For this reason, individual proxies that make up a service mesh are sometimes called “sidecars”, since they run alongside each service, rather than within them. Taken together, these “sidecar” proxies—decoupled from each service—form a mesh network.
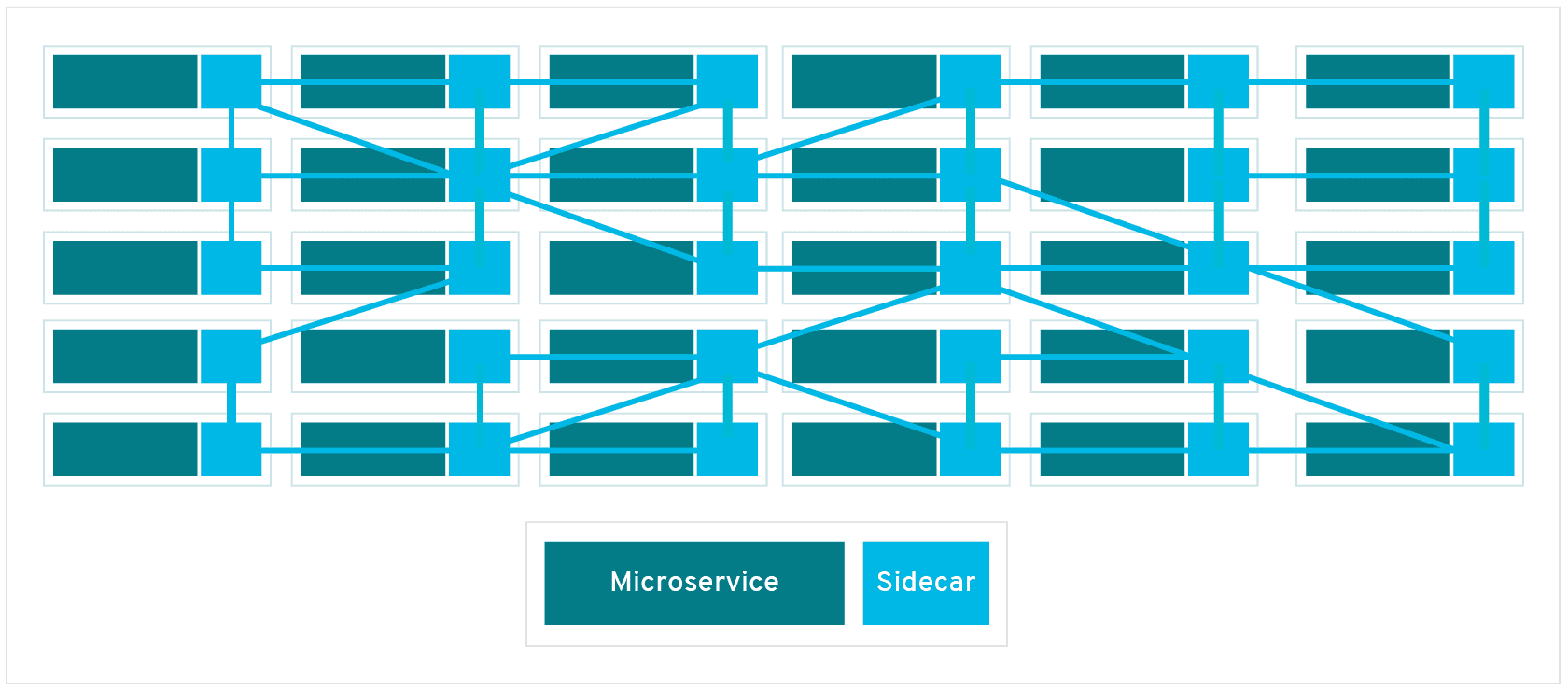
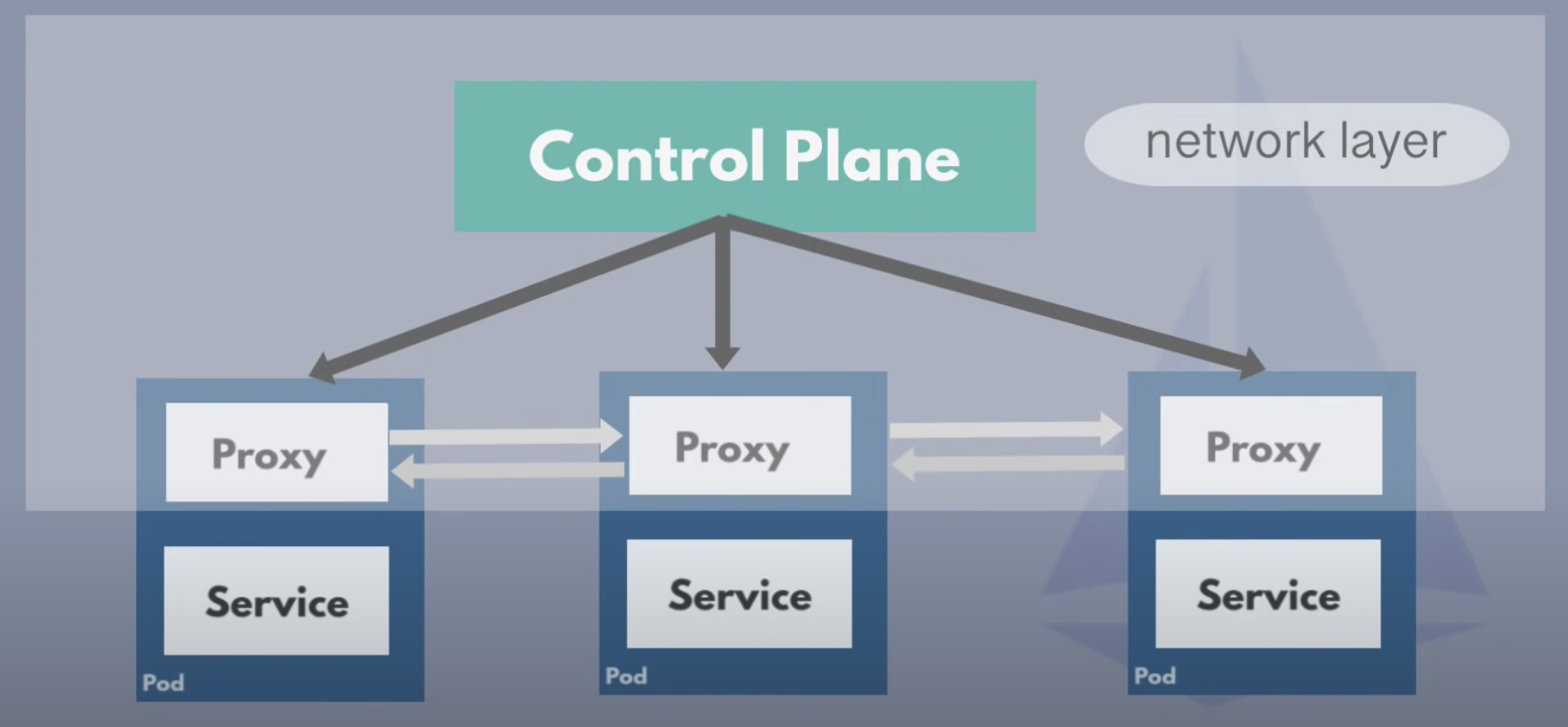
Why Service mesh -> lstio
- Starting with a question: Kubernetes defines the final state of the service and enables the system to reach and stay in that state automatically. So how do you manage the traffic on the service after the application has been deployed?
- There are limitations with K8s K8s is used as a tool for intensive resource management. However, after allocating resources to the application,K8s doesn’t fully solve the problems of how to ensure the robustness and redundancy of the application, how to achieve finer-grained traffic division (not based on the number of instances of the service), how to guarantee the security of the service, or how to manage multiple clusters, etc.
lstio 101
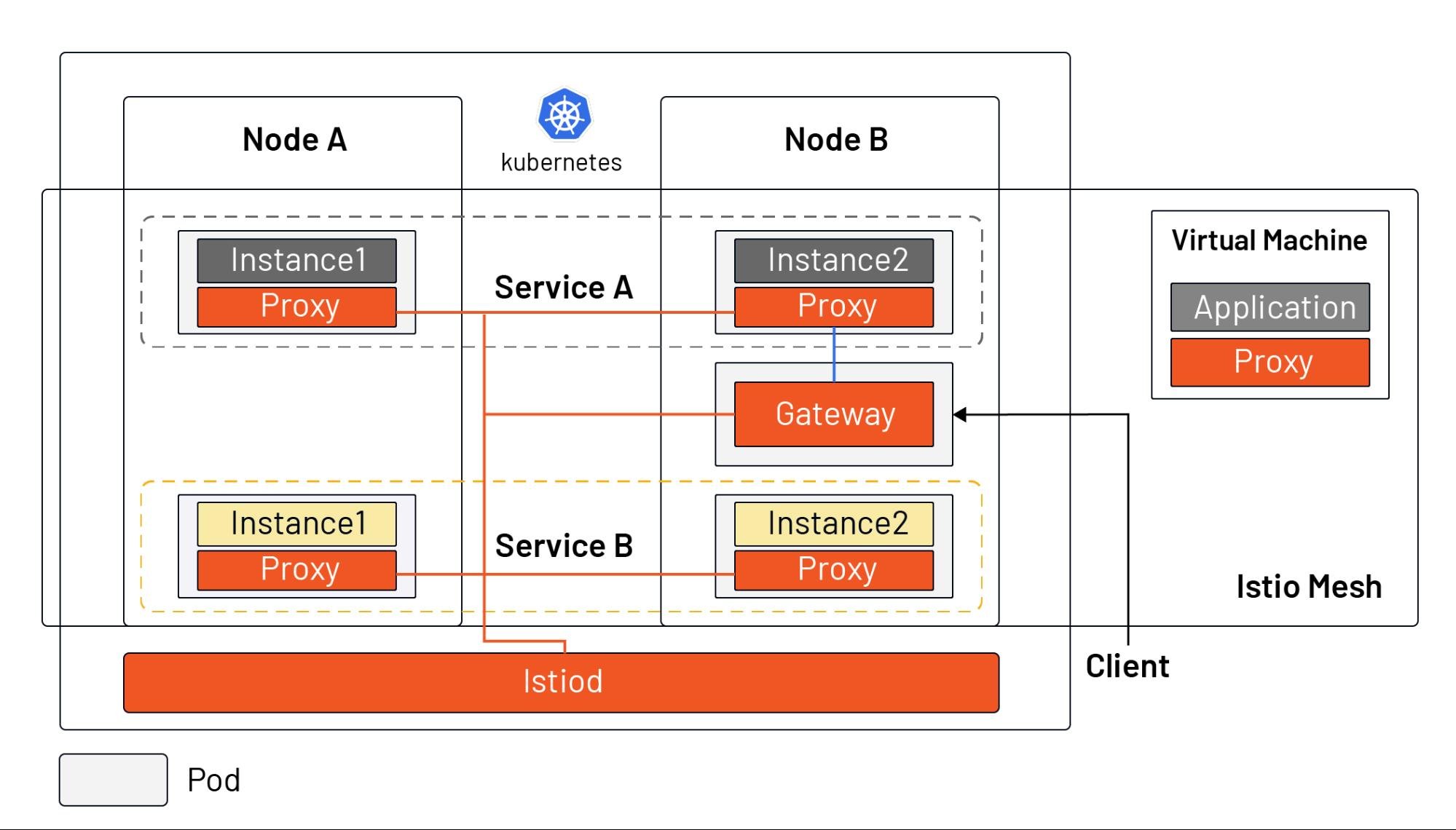 From the diagram we can see that:
From the diagram we can see that:
Istiodacts as the control plane, distributing the configuration to all sidecar proxies and gateways. (Note: for simplification, the connections between Istiod and sidecar are not drawn in the diagram.)- Istio enables intelligent application-aware load balancing from the application layer to other mesh enabled services in the cluster, and bypasses the rudimentary kube-proxy load balancing.
- Application administrators can manipulate the behavior of traffic in the Istio service mesh through a declarative API, in the same way they manage workloads in Kubernetes. It can take effects within seconds and they can do this without needing to redeploy.
- Ingress is replaced by Gateway resources, a special kind of proxy that is also a reused Sidecar proxy.
- A sidecar proxy can be installed in a virtual machine to bring the virtual machine into the Istio mesh.
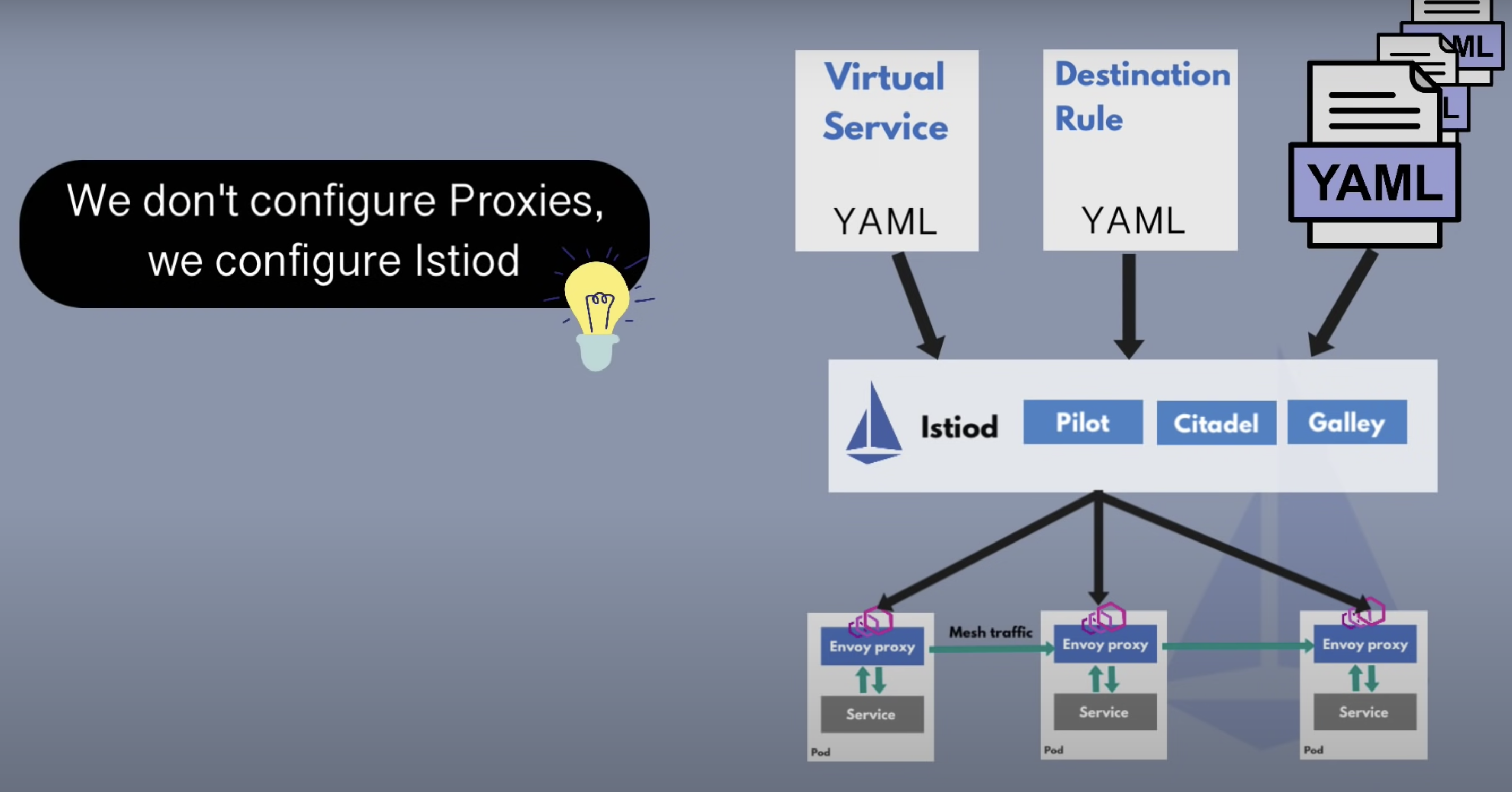
Summary
- Service Mesh is the cloud native equivalent of TCP/IP, addressing application network communication, security and visibility issues.
- Istio is currently the most popular service mesh implementation, relying on Kubernetes but also scalable to virtual machine loads.
- Istio’s core consists of a control plane and a data plane, with Envoy as the default data-plane agent.
- Istio acts as the network layer of the cloud native infrastructure and is transparent to applications.
514 Words
2022-05-20 00:00